let’s get cracking with our first workbook for ISIS
ISIS TASK 1
ISIS Task Requirements 1
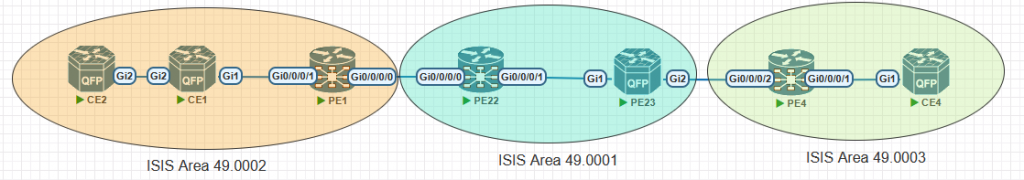
Basic configuration files have been provided with IPv4 addressing, implementing IS-IS across the multi-area network. You need to ensure proper route exchange and design segmentation between Level 1 and Level 2 areas.
ISIS Task Requirements 2
Using show commands ensure that the routers have the correct ISIS level neighbours
Using show commands ensure the level 2 routers have the correct routes
Using show commands ascertain if the level 1 routers have the level 2 routes
Use ping commands to check connectivity
Save your ISIS configurations for the next workbook
As we can see here we have our first task you’ve been provided with the IPv4 addressing So all the configurations for that are done So there’s basic connectivity between each pair of devices.
So we need to implement ISIS across the multi area network and we need to ensure proper route exchange and design the segmentation between levels 1. And level 2 areas.
Task1 Level Solutions
CE2 to CE1 L1 only
CE1 to PE1 L1 only
PE1 to PE22 L2 only
PE22 to PE23 L2 only
PE23 to PE4 L2 only
PE4 to CE4 L1 only
what we’re gonna do with this is we’re going to decide what we’re going to have as our levels. as CE 2 is at the end of the area and It’s not linking with, another area, this can be a level 1 device and exactly the same with CE 1 So that can also be a level 1 device.
However, if we was to select PE 1 as a level 1 device, then that would mean it can’t form a neighbor ship with PE 22 because that’s in a different area. So we have a couple of options available, we can either set it as a level 2 device only, which is absolutely fine or we can set it as default to be a level 1 level 2 router. Now, if we do that and that’s a normal implementation, you’ll see that quite often.
Then what that would mean is that between CE 1 and PE 1, you will have both a level 1 membership. if we set this to level 1 anyway that’s all you’ll have, but you’ll still be getting updates still being tried to send out for level 1 towards CE 1.
To try and minimise the amount of traffic again with this particular scenario, it’s not a very big lab, but in a bigger production network you may decide that you don’t want to be propagating in additional level information just for it to be dropped on the other side, so we will set this as a level 2 router
and exactly the same for PE 22, and 23 as these are both basically ABRs, on their respective areas. We we have a PE 22 connected from area one to area two and PE 23 connecting from area 0001 to area 0003 so we can set these as level 2 devices
We put that as a level 2 and that as a level 2 because they’re direct neighborships in different areas towards PE 1 and towards PE 4. Don’t need to have level 1 information at all and again with PE 4
And but we can just do level 1 between PE 4 and CE 4 let’s implement that and see if we can get this up and running.
let’s start on CE 2 We’ll work from left and work our way across
ISIS Conifguration
ISIS Configuration Solution
CE2#
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0002.00
is-type level-1
passive-interface Loopback0
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-1
CE1#
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0001.00
is-type level-1
passive-interface Loopback0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-1
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-1
PE1#
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0011.00
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface Loopback0
passive
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
circuit-type level-1
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
PE22#
router isis 1
net 49.0001.0000.0000.0022.00
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface Loopback0
passive
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
PE23#
router isis 1
net 49.0001.0000.0023.00
is-type level-2-only
passive-interface Loopback0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-2-only
PE4#
router isis 1
net 49.0003.0000.0044.00
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface Loopback0
passive
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
circuit-type level-1
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
CE4#
router isis 1
net 49.0003.0000.0004.00
is-type level-1
passive-interface Loopback0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip router isis 1
isis circuit-type level-1
Okay It’s going to enable mode the first thing we need to do is get our ISIS
neighborship up and running, and that’s going to be on Router CE 2. we need to set our ISIS Net address up This is for area 49.0002 So let’s go into configuration mode
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0002.00
is-type level-1
passive-interface Loopback0That means while the routes for loopback 0 will be advertised it won’t attempt to form any particular sort of neighborships. So that’s all we really need to do just to get IS IS up and running What we need now is to add in the physical interface that’s going to connect CE 2 to CE 1.
interface GigabitEthernet2
description link to CE1
ip address 10.10.21.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
isis circuit-type level-1let’s now jump on to CE 1. And do the same thing We’ll do the membership between CE 1 and CE 2 first
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0001.00
passive-interface Loopback0interface GigabitEthernet1
description link to PE1
ip address 10.10.11.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
isis circuit-type level-1
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
description link to CE2
ip address 10.10.21.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
negotiation auto
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
isis circuit-type level-1Now, the neighborship is obviously not formed yet because we’ve not put the g2 interface into the actual ISIS router protocol
We see our adjacency has now come up So that’s fantastic We can do a do show IP route ISIS And we can see that it’s learned the loop back here from CE 2 So that’s good we have our first neighborship up We’ll jump along now to the next device and sorry the to the next neighborship, which is on g1 and we’ll get that up and running as well
CE1#show ip route isis
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L1 2.2.2.2 [115/10] via 10.10.21.2, 06:11:51, GigabitEthernet2So let’s go into interface g1 and let’s do our ISIS configuration
CE1#show isis nei
CE1#show isis neighbors
Tag 1:
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
CE2 L1 Gi2 10.10.21.2 UP 9 CE2.01
PE1 L1 Gi1 10.10.11.11 UP 7 PE1.03
CE1#So that is now CE 1 done now let’s jump on to PE 1 which is our Cisco IOS XR device and get ISIS running on this
router isis 1
net 49.0002.0000.0011.00
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
interface Loopback0
passive
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
circuit-type level-1
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
!
And let’s sit there now
So let’s do
router ISIS one
Okay Let’s do our next statement. So it’s gonna be forty nine dot zero zero two
dot zero zero zero zero dot zero zero zero zero. Actually it’s still eleven dot zero zero. that’s our next statement. That’s fine what we need to do we need to add in the IPv4 address family as well. The address family IPv4 unicast
So we need to globally activate it And let’s do our interface loop back zero and we’ll set that to passive
And we also need to add the interface as well into the IPv4 address family
To address family IPv4 unicast
Okay excellent. So now we’ve added in the loopback We need to add in our interfaces. So gig one is going to be a level one interface
So let’s do interface g zero slash zero slash zero slash one
And we’re going to do the address family as well but we need to set the actual circuit type as well. So let’s do the circuit type
and we’ll do
level one and the address family is going to IP b for unicast Okay
Now let’s jump on to the interface that goes to p e 22 which is gig zero
So interface g zero slash zero slash zero and the circuit type. At this time this is going to be a level two because you can’t do a level one adjacency with a device in a different area
So level two, and the address family is I p v for unicast and let’s commit that
Let’s have a look at our
ISIS configuration So we have our net statement We have the global address family IPv4 unicast. We have our interface loop back zero. It’s passive, so it won’t attempt to try and form any lever ships on that. We’ve again added in the IPv4 unicast Gig of ethernet zero We’ve set that to level two with the address family and gig of ethernet one We’ve set that to level one. Okay.
So on CE one there we go We see that the Labororship has come up so that’s great So let’s jump on to PE 22 now and see what we can do with this So with PE 22, we have gig zero and gig one They are both level two
Connections and it’s in area one. let’s get cracking with this one
So let’s go
Comf t, and let’s do router ISIS process one. But the process is only the process ID is only locally significant. So yeah you can use any process ID that you want You don’t have to keep the same one but just when you’re lagging sometimes it’s easier to just do that
And then we’re going to do address family IPv4 unicast to enable it globally and we’re going to interface loop back zero It’s gonna be passive
Okay That’s fantastic And we just need to add in the address family again, the address family IPv4 unicast
Brilliant. we know that both gig ethernet zero and gig ethernet one are both going to be level two So zero and one. So let’s do interface g zero slash zero slash zero slash zero. And the circuit type is sorry level two rather is going to be level two
and the Just family is going to I b e v four unicast Okay
And interface g zero slash zero slash zero slash one
And the circuit type, again is going to be level two
And your dress family is I p v four unicast Okay Let’s commit that
Alright Fantastic Let’s do a show ISIS
neighbor And we can see that we already have a neighbor ship with e e one We can see that it’s a level two neighbor ship and that’s exactly what we’re expecting to see Let’s jump on to p e 23. P 23 is an iOS XE router. So let’s do g. So again g one and g two They’re both going to be level two. So let’s jump on to that
So go enable comptee
and let’s do a
router
ISIS
one Let’s do a net statement of forty nine dot zero zero zero one
zero zero zero zero zero zero zero
23 two zero
Okay And let’s do
passive interface loopback zero
that’s the interface in So we we need to add in now the actual interfaces the physical interfaces And just before we do that I just want to quickly check p e 22 again
Just to double check what I put down as the IS IS Okay Yeah I put that down This is the correct. neighborship No That’s fine
Brilliant stuff let’s jump back on p 22, and let’s get out of that, and let’s go into interface g one
and ISIS
Type oops It won’t want
So let’s put that back in again
So ISIS
circuit type Is level two
and IP router
ISIS process one
Okay And let’s go on to interface g two and we see we have our neighborship with p 22 already which is great. So g two and it’s going to be ISIS circuit type is going to be level two
and IP router
ISIS process one
that’s p e 22
Done as well and p e 23 are both done. Brilliant
Okay Let’s jump on to the
next router
and see what’s going on with that one
Okay We did see a neighbor ship come up on p e 23 So it’s possible I may have already configured this one Let’s have a look
Alright Okay. So I have already enabled this which is fine It’s supposed it just keeps the, the router the
video for being exceptionally long. So again exactly what we expect. So gig ethernet two, we’ve set that to level two, and we’ve also set gig ethernet one which is going to CE one to level one. We have our passive interface there, and we have our next statement which is exactly what we want. let’s do a show ISIS neighbor and see what’s happening with that So we’ll have our level two neighborship with p e 23 Which is exactly what we expect.
Okay In that case please let’s jump on to a c four
And so show iOSize neighbor You see nothing Okay. It should run
section ISIS we have no ISIS isn’t it Let’s set this one up then So confit
And let’s go into router
ISIS one
and the next statement is going to be forty nine dot zero zero zero three zero zero zero zero zero
Forty four
There we go Alright Sweet. And let’s do passive interface loopback zero
Okay And now let’s go on to our
physical interface, which is g1
Interface g 1
and we do
ISIS circuit type level 1
and IP router ISIS process ID 1
Okay. Fantastic. And then we see we have our adjacency has now come up to
PE4
we’ve now done the first task.
we need to do our show commands as we’ve done the first task we’ve been we’ve that are individual area neighbor our levels, and we’ve got the neighborships up and running. So what we need to do now is to use our show commands to see whether or not we have our neighborships up and whether we are actually learning a route. So let’s jump on to let’s say PE 1
and let’s do a
show ISIS database
PE 1 has a neighborship on the level 1 and the level 2 we have two different databases. We have level 1 database and we have the level 2 database as well. And we can see the actual neighbor that we have on that If we want to have a look at the details which we can
and it’ll show us more detail of the actual level 1 and level 2 routes users like private instance. We can see that we’re learning the let’s say the 1.1.1.1 address. We can see the metrics that is coming from, and
the interfaces there that we’re learning it from and the hashes for the actual LSP updates itself. there’s a lot of information. Let’s have a look at show route
ISIS to see what we’re learning. we can see we’ve got the loopback of CE 1 We have the loopback of of CE 2 under pair. The loopback of PE 4
So we we’re getting a lot of the loopbacks and a lot of the routes so that’s absolutely great That’s exactly what we expect to see. Let’s have a look on PE 22 now
Okay Let’s do a
show ISIS neighbor
we have our two neighborships up and running They’re both level 2 which is what we wanna see. Show, show route ISIS
Again we can see that we’re we’ve got the loopbacks in there so that’s looking exceptionally good. of of good note here is that if I’m gonna say we have the loopback of CE 4 and PE 4 in there So CE 4is PE 4. So we have the loop back so everything’s going great in that regard. Let’s have a look on CE 1 the iOS-XR image so CE 1 That was this device here remember this only has a level 1 adjacency with PE 1
So let’s have a look here So let’s do a Show IP interface brief
So the loopback 1.1.1.1 Okay But we we’ve seen that here So that’s been learnt
on PE 22
show IP route ISIS
And it’s been learnt as well on PE 23. So even though the membership between CE one and PE one is level one only
PE 1 has taken the level 1 routes and is propagated over to PE 22 and PE 23, and it will be propagated back over to PE 4 as well So that’s the exact, behaviour we expect to see However what we was interested in was CE 1 So let’s have a look at CE 1 and see what it knows. So let’s do a show IP route ISIS
the only route that it’s learned through ISIS is the loopback of CE 1 and the loopback of PE 1 It’s not learned anything else It’s not learned any of the level 2 routes all it’s learned to do the level 1 routes This is a bit of a gotcha when you’re dealing with, especially iOS-XR
is that it while it will take level 1 routes and propagate them into level 2 it doesn’t do it the other way around so we need to fix that But that is for another episode which will be coming up after this.

Pingback: Introduction to the CCNP and CCIE Workbooks - RichardKilleen
Pingback: Workbook 2 ISIS IPv4 Troubleshooting with Route Policies, Authentication - RichardKilleen